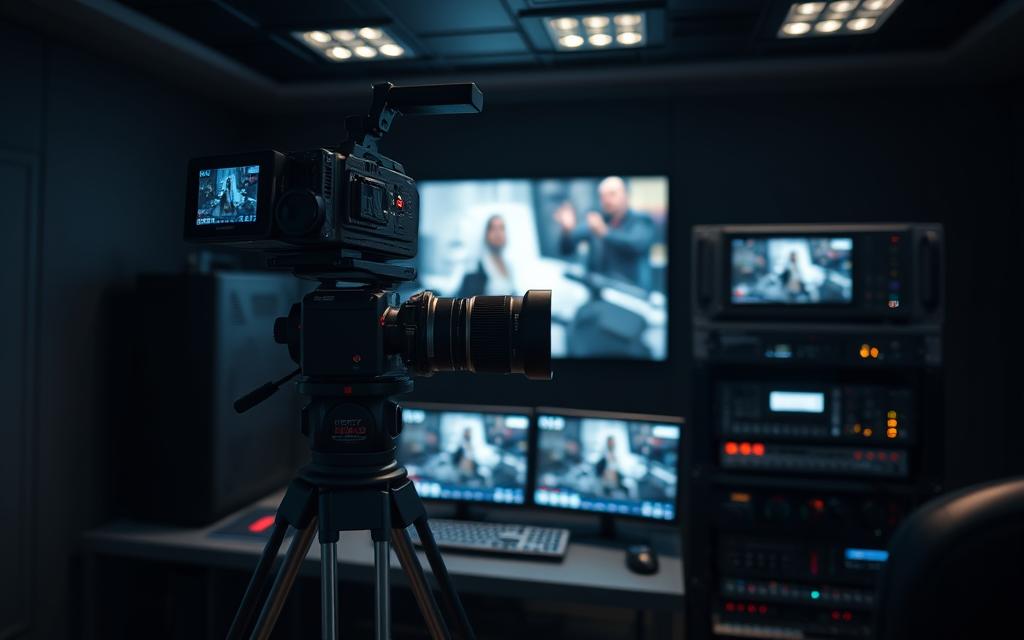
In professional broadcast settings, sending video without errors is key. High-Definition Serial Digital Interface (HD-SDI) is a standard for sending HD video and audio without compression.
It follows SMPTE 292M standards, reaching speeds of 1.485 Gbit/s. HD-SDI ensures clear signals over coaxial or fibre optic cables.
The serial digital interface is built for tough tasks. It’s used in TV studios, live events, and medical imaging.
HD-SDI has low latency and fights against compression issues. It keeps video quality high over 100 metres, unlike lower-grade options.
This makes HD-SDI vital for situations where perfect video is essential. It’s a cornerstone in many industries.
What is HD-SDI Technology: Core Concepts
HD-SDI technology is about its technical details and how it evolved. It’s a big step in improving broadcast quality. It builds on years of work in digital video standards.
Defining High-Definition Serial Digital Interface
HD-SDI is a top standard for sending digital video and audio without compression. It uses 75-ohm coaxial cables with BNC connectors to keep signals strong over long distances.
It follows the SMPTE 292M standard from 1998. HD-SDI can send signals at 1.485 Gbit/s. This lets it handle high-definition formats like 720p and 1080i without losing quality.
This technology works well with older systems but is better in many ways. It’s made to be reliable in places where quality is key.
The Historical Development from SDI to HD-SDI
The move from SDI to HD-SDI was a big change in broadcast tech. It met the need for clearer, higher resolution content.
Standard Definition Digital Interface Foundations
SDI started the journey to modern digital video. It was set in 1989 as SMPTE 259M. It handled standard definition signals like 480i and 576i.
SD-SDI worked at 270 Mbit/s. It brought new ideas like embedded audio and error checking. These became important for future tech.
This tech moved from old composite video to digital component signals. The use of coaxial cables with BNC connectors helped future upgrades.
Advancement to High-Definition Standards
Going to high-definition needed big tech jumps. The SDI to HD-SDI evolution needed faster data rates and better signal quality. It also needed better error correction.
New methods for equalising signals and recovering clocks were created. These helped HD content travel reliably. They kept the familiar BNC connector setup.
HD-SDI changed the game for broadcasting and production worldwide. It became the mainstay of HD TV broadcasting. It helped the world switch to HD content.
Knowing about HD-SDI history helps us understand today’s video tech. The standards from this time shape today’s broadcast systems and equipment.
Technical Specifications and Standards
HD-SDI technology works at a bit rate of 1.485 Gbit/s. It supports high-definition video formats like 720p and 1080i. This ensures video signals are sent efficiently with little delay.
Thanks to SMPTE standards, we now have faster options. Dual link HD-SDI, defined by SMPTE 372M, uses two links for 3 Gbit/s. The 3G-SDI standard, SMPTE 424M, offers a single-link 3 Gbit/s option. This makes setting up easier without losing quality.
Important features include NRZI encoding for signal quality and synchronisation packets (TRS) for timing. Video payload encoding uses YCbCr 4:2:2 colour space for true colours. Ancillary data spaces carry audio, timecode, and metadata, supporting up to 16 audio channels.
New standards like 6G-SDI and 12G-SDI support ultra-high definition like 4K and 8K. They boost the interface’s abilities for professional use in broadcasting and production.